As the teas test for dental hygiene takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with an engaging tone into a world crafted with expertise, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Delving into the depths of this topic, we will explore the intricate relationship between tea’s composition and its profound impact on oral health. From understanding the chemical components that interact with oral bacteria to unraveling the varying effects of different tea types, this exploration promises to shed light on tea’s potential as a complementary or alternative dental hygiene aid.
Tea’s Composition and Dental Hygiene
Tea is a popular beverage enjoyed worldwide, and it has been found to have numerous health benefits, including promoting dental health. Tea contains several chemical components that interact with oral bacteria and contribute to its dental hygiene properties.
Tea Polyphenols
Tea polyphenols, such as epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), are powerful antioxidants that inhibit the growth of oral bacteria. Studies have shown that EGCG can prevent the formation of dental plaque and reduce the risk of cavities and gum disease.
Fluoride
Tea is a natural source of fluoride, which is an essential mineral for dental health. Fluoride helps to strengthen tooth enamel and prevent tooth decay.
Tannins
Tannins are astringent compounds found in tea that can help to reduce inflammation and bleeding in the gums. They also have antibacterial properties that can help to prevent gum disease.
Catechins
Catechins are another group of polyphenols found in tea that have been shown to have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. They can help to reduce the risk of cavities and gum disease.
Types of Teas and Their Effects on Dental Health: Teas Test For Dental Hygiene
Tea, a popular beverage enjoyed worldwide, comes in various types, each with unique effects on oral health. Understanding these variations can help you make informed choices to maintain a healthy smile.
Black Tea
Black tea, known for its robust flavor, contains tannins, antioxidants that can inhibit the growth of bacteria responsible for plaque and cavities. Studies suggest that regular consumption of black tea may reduce the risk of gum disease and tooth decay.
Teas test for dental hygiene is an essential exam to maintain oral health. If you’re seeking additional resources on the topic, I recommend checking out the level l reading plus answers for further insights. These answers provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter, allowing you to delve deeper into the intricacies of teas test for dental hygiene and enhance your knowledge in this crucial area.
Green Tea
Green tea, rich in catechins, has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds can help fight oral bacteria, reduce inflammation in the gums, and protect against tooth decay. Some studies have even shown that green tea extract can inhibit the formation of cavities.
Herbal Teas
Herbal teas, made from various plants and herbs, offer a range of potential benefits for oral health. Some herbs, such as peppermint and chamomile, have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. Others, like licorice root, may help soothe oral discomfort and reduce gum inflammation.
Considerations
While certain teas can promote dental health, excessive consumption of any type of tea can lead to negative effects. The high caffeine content in black and green teas can contribute to tooth erosion and dehydration, so moderation is key. Additionally, some herbal teas may interact with medications or have other potential side effects, so consulting a healthcare professional before consuming them is advisable.
Tea Consumption Methods and Dental Hygiene
Tea, a popular beverage enjoyed worldwide, can be consumed in various ways, each influencing its impact on dental hygiene.
Hot Tea
Hot tea, a common method of consumption, can have a positive effect on oral health. The warmth of the tea stimulates saliva production, which helps neutralize acids in the mouth and reduce the risk of cavities. Additionally, the tannins present in tea have antibacterial properties that can inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria.
Cold Tea
Cold tea, while not as effective as hot tea, can still provide some benefits. The tannins in cold tea can still inhibit bacterial growth, but the lack of warmth reduces saliva production, which can lead to a slightly increased risk of cavities.
Tea with Additives
Adding sweeteners or milk to tea can alter its effects on dental hygiene. Sugar, a common sweetener, can promote tooth decay, while milk can neutralize the acids in tea, reducing the risk of cavities.
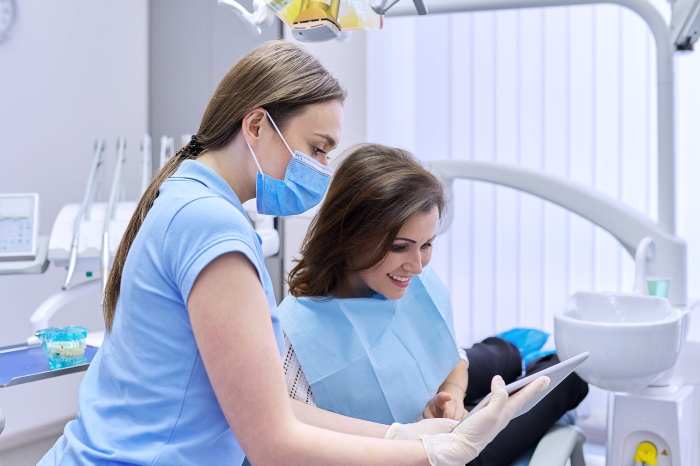
Tea’s Role in Plaque and Tartar Prevention
Tea, with its wealth of polyphenols, plays a crucial role in preventing the formation of plaque and tartar. These polyphenols inhibit the growth of bacteria that cause dental caries and periodontal disease.
Inhibition of Bacterial Growth
Tea polyphenols, particularly catechins, have antibacterial properties that effectively inhibit the growth of Streptococcus mutans, the primary bacteria responsible for plaque formation. By reducing bacterial colonization, tea consumption helps prevent the accumulation of plaque on tooth surfaces.
Reduction of Plaque Formation
Studies have demonstrated the efficacy of tea in reducing plaque buildup. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Dentistry found that participants who consumed black tea for 12 weeks showed a significant reduction in plaque accumulation compared to the control group.
Prevention of Tartar Formation
Tartar, or calculus, is a hardened deposit that forms on teeth when plaque is not removed regularly. Tea polyphenols inhibit the formation of tartar by preventing the crystallization of calcium and phosphate ions. By reducing plaque accumulation and inhibiting tartar formation, tea helps maintain good oral hygiene and prevent dental problems.
Tea’s Effects on Oral Microbiota

Tea consumption can influence the composition and diversity of oral microbiota, the community of microorganisms residing in the oral cavity. The polyphenols present in tea exhibit antimicrobial and antioxidant properties, affecting the growth and activity of oral bacteria.
Altered Microbial Composition
- Tea consumption has been associated with a reduction in the abundance of cariogenic bacteria, such as Streptococcus mutansand Lactobacillus acidophilus, which contribute to tooth decay.
- Conversely, tea may promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, including Lactobacillus reuteriand Streptococcus salivarius, which help maintain oral health.
Enhanced Microbial Diversity
Tea consumption can increase the diversity of oral microbiota, reducing the dominance of certain bacterial species. This enhanced diversity is associated with improved oral health, as it promotes a more balanced and resilient microbial ecosystem.
Potential Implications for Dental Hygiene
The alterations in oral microbiota composition and diversity induced by tea consumption may have implications for dental hygiene and overall oral health:
- Reduced cariogenic bacteria may lead to a decreased risk of tooth decay.
- Increased beneficial bacteria may enhance the oral immune response and protect against periodontal disease.
- Enhanced microbial diversity may promote a healthier oral ecosystem, reducing the likelihood of oral infections.
Tea’s Potential as a Dental Hygiene Aid
Tea, with its rich composition of bioactive compounds, has shown promising potential as a complementary or alternative dental hygiene aid. It offers several advantages, including:
-
-*Antibacterial and antimicrobial properties
Tea contains polyphenols, such as catechins and theaflavins, which exhibit antibacterial and antimicrobial effects against oral pathogens, including Streptococcus mutans and Porphyromonas gingivalis, known to cause dental caries and periodontal disease.
-*Anti-inflammatory properties
Tea’s polyphenols possess anti-inflammatory properties, reducing inflammation in the oral cavity, which is a major contributing factor to periodontal disease and other oral health issues.
-*Antioxidant properties
Tea’s antioxidants, such as flavonoids, help protect oral tissues from oxidative stress, a significant factor in dental erosion and aging.
However, it’s important to note that tea alone cannot replace regular dental hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing. Excessive consumption of tea can lead to tooth staining, and its potential effects on dental health may vary depending on the type of tea, preparation methods, and individual factors.
Future Research Directions
While significant progress has been made in understanding the role of tea in dental hygiene, further research is needed to fully elucidate its potential benefits and limitations.
Specific areas that warrant further investigation include:
Tea’s Role in Preventing Caries
- Longitudinal studies to assess the impact of regular tea consumption on caries incidence and progression.
- In vitro and animal studies to determine the mechanisms by which tea inhibits cariogenic bacteria and biofilm formation.
- Clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy of tea-based mouthwashes and dentifrices in preventing caries.
Tea’s Effects on Periodontal Health
- Longitudinal studies to determine the association between tea consumption and periodontal disease prevalence and severity.
- Animal studies to investigate the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of tea on periodontal tissues.
- Clinical trials to assess the efficacy of tea-based therapies in reducing periodontal inflammation and improving periodontal health.
Tea’s Potential as a Dental Hygiene Aid, Teas test for dental hygiene
- In vitro studies to evaluate the antimicrobial activity of different tea extracts against oral pathogens.
- Clinical trials to assess the effectiveness of tea-based mouthwashes and dentifrices in reducing oral bacteria and improving oral hygiene.
- Studies to explore the potential use of tea as a natural alternative to conventional fluoride treatments.
Tea’s Long-Term Effects on Dental Health
- Longitudinal studies to investigate the cumulative effects of tea consumption on dental health over time.
- Studies to assess the potential risks and benefits of long-term tea consumption, particularly with regard to staining and tooth erosion.
- Studies to develop guidelines for safe and effective tea consumption for optimal dental health.
FAQ Compilation
Can tea consumption replace regular brushing and flossing?
No, while tea can complement dental hygiene practices, it cannot replace the mechanical removal of plaque and bacteria achieved through brushing and flossing.
Which type of tea is most effective for dental hygiene?
Green tea, with its high concentration of catechins, has been shown to possess the most beneficial effects on oral health.
How often should I consume tea for dental hygiene benefits?
Consuming tea 1-2 times per day can provide significant benefits for oral health.