Embark on a linguistic adventure with gramática a Answer Key Level 2, your comprehensive guide to unraveling the intricacies of grammar. Dive into the fundamental principles that govern language, gaining a deeper understanding of how words and phrases interact to convey meaning.
This resource delves into the building blocks of grammar, exploring the different types and functions of grammar, as well as the grammatical structures and rules that shape our communication. By mastering these concepts, you’ll elevate your language skills, enabling you to express yourself with precision and clarity.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Grammar is the study of the structure and rules of a language. It provides a framework for understanding how words and phrases are combined to form meaningful sentences. Grammar encompasses various components, including syntax, morphology, and semantics.
Syntax refers to the rules that govern the arrangement of words and phrases within a sentence. It determines the order and relationship between different parts of speech, ensuring grammatical correctness and coherence.
Types of Grammar
There are several types of grammar, each with a specific focus:
- Descriptive grammardescribes the structure and rules of a language as it is currently used.
- Prescriptive grammarprescribes how a language should be used, often based on traditional or formal standards.
- Theoretical grammarexplores the underlying principles and theories that govern language structure.
- Historical grammarexamines the evolution of a language’s grammar over time.
Grammatical Structures and Rules: Gramática A Answer Key Level 2
Language is a complex system of communication that uses various grammatical structures and rules to convey meaning. These structures and rules govern the arrangement and usage of words, phrases, and sentences, enabling us to express ourselves clearly and effectively.
Grammatical structures refer to the fundamental building blocks of language, such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs. These structures are combined according to specific rules to form meaningful sentences and phrases. For example, in English, sentences typically follow a subject-verb-object structure, where the subject performs an action (verb) on an object.
Parts of Speech
Parts of speech are the basic categories into which words are classified based on their function in a sentence. The most common parts of speech include:
- Nouns: Refer to people, places, things, or ideas.
- Verbs: Express actions, events, or states of being.
- Adjectives: Describe or modify nouns.
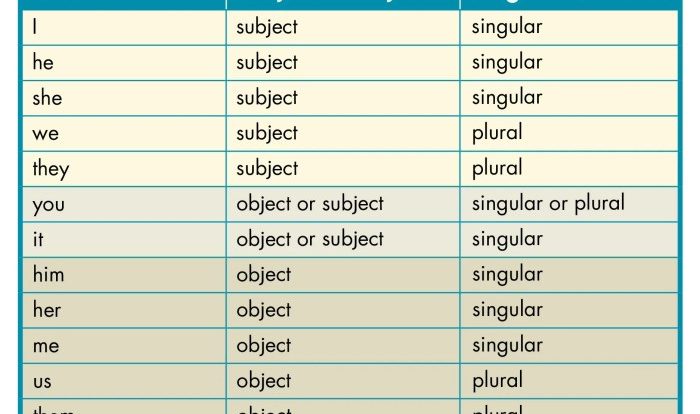
- Pronouns: Replace nouns to avoid repetition.
- Prepositions: Show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in the sentence.
- Conjunctions: Connect words, phrases, or clauses.
- Interjections: Express strong emotions or reactions.
li> Adverbs: Describe or modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
Sentence Structure
Sentences are the basic units of communication in language. They consist of a subject, a verb, and optionally, an object. The subject performs the action expressed by the verb, while the object receives the action.
There are four main types of sentences:
- Declarative sentences: Make a statement.
- Interrogative sentences: Ask a question.
- Imperative sentences: Give a command or request.
- Exclamatory sentences: Express strong emotion.
Phrase Structure
Phrases are groups of words that do not contain a subject and a verb. They can function as nouns, verbs, adjectives, or adverbs.
There are three main types of phrases:
- Noun phrases: Act as nouns.
- Verb phrases: Act as verbs.
- Adjective phrases: Act as adjectives.
- Adverb phrases: Act as adverbs.
Conclusion
Grammatical structures and rules are essential for effective communication. They provide a framework for organizing and expressing our thoughts and ideas in a clear and meaningful way. By understanding and applying these structures and rules, we can improve our communication skills and express ourselves more effectively.
Parts of Speech and Their Functions
Parts of speech are the building blocks of language, and they play specific roles in sentences. Understanding the different parts of speech and their functions is essential for effective communication.
The main parts of speech include nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Each part of speech has a unique function and contributes to the overall meaning and structure of a sentence.
Nouns, Gramática a answer key level 2
Nouns are words that name people, places, things, or ideas. They can be proper nouns (specific names, like “John” or “New York”) or common nouns (general names, like “boy” or “city”).
- Example:The dogbarked at the mailman.
Verbs
Verbs are words that describe actions, states of being, or occurrences. They are the heart of a sentence and indicate what is happening.
- Example:The boy ranto the store.
Adjectives
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns. They provide additional information about the qualities or characteristics of something.
- Example:The tall manwalked down the busy street.
Adverbs
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They provide information about how, when, where, or to what extent something is done or described.
- Example:The cardrove slowlydown the road.
Sentence Structure and Syntax
Sentences are the building blocks of language, conveying ideas and information. They are organized according to specific rules, known as syntax, which govern how words are arranged to form meaningful units.
Structure of Sentences
Sentences typically consist of two main components: a subject and a predicate. The subject identifies what or who the sentence is about, while the predicate describes an action, state, or quality associated with the subject.
Types of Sentences
There are various types of sentences, each with its unique structure and purpose:
- Declarative sentencesmake statements or assertions.
- Interrogative sentencesask questions.
- Imperative sentencesexpress commands or requests.
- Exclamatory sentencesconvey strong emotions or surprise.
Importance of Syntax
Syntax is crucial for clear and effective communication. It ensures that sentences are grammatically correct and that their intended meaning is conveyed accurately. Proper syntax allows readers or listeners to understand the relationship between words and phrases within a sentence, facilitating comprehension and avoiding ambiguity.
Punctuation and Style
Punctuation and style are essential elements of grammar, playing a crucial role in shaping the meaning, clarity, and impact of written communication. Punctuation marks, such as periods, commas, semicolons, and quotation marks, provide structure and organization to text, making it easier for readers to comprehend and interpret.
Different styles of writing, such as academic, journalistic, or creative, have their own distinct grammatical conventions and stylistic preferences, influencing the tone, formality, and purpose of the writing.
Punctuation Marks
Punctuation marks serve various functions in grammar:
- Periods (.): Denote the end of a complete sentence, indicating a pause or full stop.
- Commas (,): Separate items in a list, indicate pauses within sentences, and set off introductory elements or dependent clauses.
- Semicolons (;): Connect closely related independent clauses or separate items in a list that contain commas.
- Quotation marks (” “): Enclose direct quotations and titles of creative works.
Writing Styles
Different writing styles have distinct grammatical conventions and stylistic preferences:
- Academic writing: Formal, objective, and evidence-based, using precise language and proper citation.
- Journalistic writing: Clear, concise, and informative, adhering to the principles of objectivity, accuracy, and timeliness.
- Creative writing: Expressive, imaginative, and often subjective, using literary devices and figurative language.
Impact of Punctuation and Style
Punctuation and style can significantly affect the meaning and clarity of written communication:
- Punctuation: Incorrect punctuation can alter the intended meaning of a sentence, making it ambiguous or even nonsensical.
- Style: The choice of writing style influences the tone, formality, and purpose of the writing, affecting how readers perceive and interpret the message.
Essential FAQs
What is the purpose of grammar?
Grammar provides the framework for language, enabling us to communicate effectively by organizing words and phrases into meaningful units.
What are the different parts of speech?
Parts of speech include nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections, each playing a specific role in sentence construction.
How can I improve my grammar?
Practice writing and speaking regularly, paying attention to grammar rules and seeking feedback to identify areas for improvement.