Nouns and articles in Spanish worksheet answers delve into the intricacies of Spanish grammar, providing a roadmap for learners to master the nuances of noun usage and article placement. This guide unravels the complexities of Spanish nouns and articles, empowering learners to navigate the linguistic landscape with confidence.
From understanding the fundamental concepts of nouns and articles to exploring the diverse types and their intricate agreement rules, this comprehensive guide serves as an invaluable resource for learners seeking to enhance their Spanish proficiency.
Nouns and Articles in Spanish
Nouns and articles are fundamental elements of Spanish grammar. They play a crucial role in conveying meaning and ensuring clarity in communication. This article provides a comprehensive overview of nouns and articles in Spanish, covering their types, usage, and agreement rules.
1. Noun and Article Basics

Nouns are words that refer to people, places, things, or concepts. Articles are words that precede nouns and indicate whether the noun is definite (specific) or indefinite (non-specific). In Spanish, there are two types of articles: definite and indefinite.
Definite articlesare used when the speaker assumes that the listener knows which specific noun is being referred to. The definite articles are el(masculine singular), la(feminine singular), los(masculine plural), and las(feminine plural).
Indefinite articlesare used when the speaker is referring to a non-specific noun. The indefinite articles are un(masculine singular), una(feminine singular), unos(masculine plural), and unas(feminine plural).
2. Types of Nouns
Spanish nouns can be classified into different types based on their meaning and function.
- Common nounsrefer to general categories of people, places, or things. Examples: casa(house), libro(book), estudiante(student).
- Proper nounsrefer to specific names of people, places, or things. Examples: María(Mary), España(Spain), El Quijote(Don Quixote).
- Abstract nounsrefer to concepts or qualities that cannot be physically seen or touched. Examples: amor(love), felicidad(happiness), inteligencia(intelligence).
- Collective nounsrefer to a group of people or things considered as a single unit. Examples: familia(family), equipo(team), multitud(crowd).
3. Types of Articles
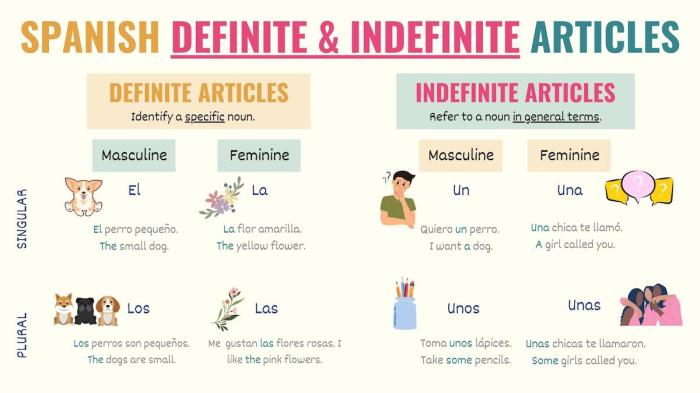
In Spanish, there are three types of articles: definite, indefinite, and partitive.
- Definite articlesare used to indicate that the noun is specific or known to the listener. Examples: el libro(the book), la casa(the house).
- Indefinite articlesare used to indicate that the noun is non-specific or unknown to the listener. Examples: un libro(a book), una casa(a house).
- Partitive articlesare used to indicate a part of a whole. Examples: de la(of the), del(of the masculine), de la(of the feminine).
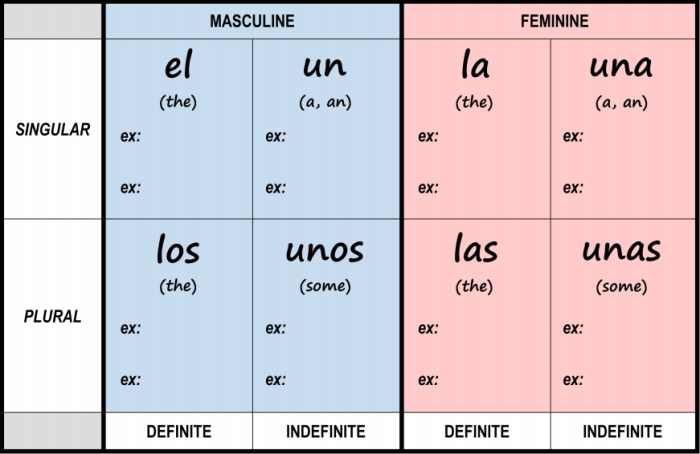
4. Noun-Article Agreement
In Spanish, nouns and articles must agree in gender and number. This means that the article used with a noun must match the gender and number of the noun.
| Noun Gender | Noun Number | Definite Article | Indefinite Article |
|---|---|---|---|
| Masculine | Singular | el | un |
| Masculine | Plural | los | unos |
| Feminine | Singular | la | una |
| Feminine | Plural | las | unas |
5. Practice Exercises: Nouns And Articles In Spanish Worksheet Answers
Exercise 1:Fill in the blanks with the correct article.
- _____ libro es muy interesante.
- _____ casa es grande y cómoda.
- _____ estudiantes son muy aplicados.
Exercise 2:Translate the following sentences into Spanish.
- The book is on the table.
- I have a new car.
- The students are studying for the exam.
6. Cultural Context
Nouns and articles play a significant role in Spanish-speaking cultures. They are used to convey respect, formality, and social relationships.
For example, the definite article elis often used before the names of people in positions of authority, such as teachers, doctors, and politicians. The indefinite article unis used before the names of people who are not well-known or who are being referred to in a general sense.
Additionally, the use of articles can vary depending on the region or country. In some Spanish-speaking countries, it is common to use the definite article before the names of days of the week and months of the year. In other countries, it is more common to omit the article.
Common Queries
What are the different types of nouns in Spanish?
Spanish nouns can be classified into various types, including common nouns (e.g., casa, libro), proper nouns (e.g., María, Madrid), abstract nouns (e.g., amor, felicidad), and collective nouns (e.g., familia, equipo).
How do articles agree with nouns in Spanish?
Articles in Spanish must agree with the gender and number of the noun they accompany. For example, “el” is used with masculine singular nouns, while “la” is used with feminine singular nouns.
What are the different types of articles in Spanish?
Spanish has three main types of articles: definite articles (el, la, los, las), indefinite articles (un, una, unos, unas), and partitive articles (de, del).