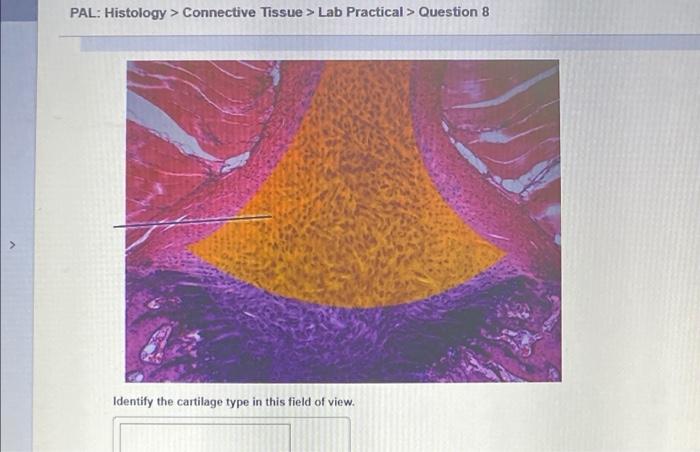
PAL Histology Connective Tissue Lab Practical Question 9 delves into the intricacies of connective tissue, a crucial component of the human body. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of connective tissue, its components, histological features, functions, and clinical significance, equipping readers with a thorough understanding of this fascinating subject.
From defining connective tissue and identifying its components to analyzing its histological features and discussing its functions, this guide offers a detailed exploration of the topic, ensuring a deep understanding of connective tissue’s role in maintaining tissue integrity and homeostasis.
Connective Tissue: Pal Histology Connective Tissue Lab Practical Question 9
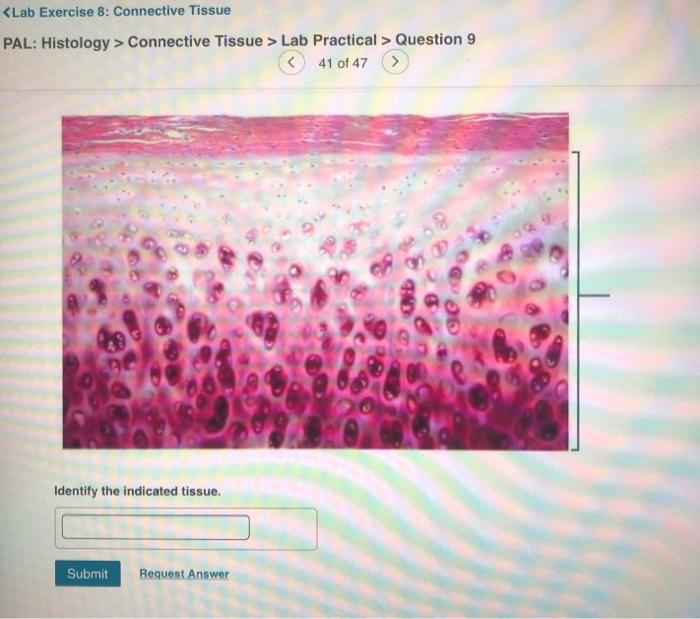
Connective tissue is a type of tissue that connects, supports, and protects other tissues and organs in the body. It is composed of cells, extracellular matrix, and fibers.
Types of Connective Tissue
- Loose connective tissue
- Dense connective tissue
- Cartilage
- Bone
- Blood
Components of Connective Tissue
Cells
- Fibroblasts
- Macrophages
- Adipocytes
- Osteoblasts
- Osteocytes
Extracellular Matrix
The extracellular matrix is a complex network of proteins and polysaccharides that provides structural support and a medium for cell communication.
Fibers
- Collagen fibers
- Elastic fibers
- Reticular fibers
Histological Features of Connective Tissue, Pal histology connective tissue lab practical question 9
Connective tissue can be identified by its histological appearance, which varies depending on the type of connective tissue.
- Loose connective tissue: Loosely arranged cells and fibers
- Dense connective tissue: Tightly packed cells and fibers
- Cartilage: Cells embedded in a matrix of collagen and proteoglycans
- Bone: Cells embedded in a mineralized matrix
- Blood: Cells suspended in a liquid matrix
Functions of Connective Tissue
- Support and protection
- Storage of energy
- Transport of nutrients and waste
- Defense against infection
- Tissue repair
Clinical Significance of Connective Tissue Disorders
Connective tissue disorders are a group of conditions that affect the structure and function of connective tissue. They can range from mild to severe and can affect multiple organs and systems in the body.
Types of Connective Tissue Disorders
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- Marfan syndrome
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lupus
Symptoms and Treatment Options
The symptoms of connective tissue disorders vary depending on the type of disorder. Treatment options may include medication, surgery, and physical therapy.
Quick FAQs
What are the main components of connective tissue?
Connective tissue comprises cells, extracellular matrix, and fibers, including collagen, elastin, and reticular fibers.
How can different types of connective tissue be distinguished based on histological features?
Histological analysis reveals variations in cell types, matrix density, and fiber arrangement, allowing for the identification of different connective tissue types.
What are the key functions of connective tissue in the body?
Connective tissue provides structural support, facilitates tissue repair, maintains homeostasis, and serves as a transport medium.