Inert minerals designed for microdermabrasion use are known as the cornerstone of this popular skin rejuvenation technique. These tiny, non-reactive particles gently exfoliate the skin’s surface, revealing a smoother, more youthful complexion.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of inert minerals for microdermabrasion, exploring their properties, applications, and safety considerations.
Inert Minerals in Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a minimally invasive cosmetic procedure that utilizes inert minerals to gently exfoliate the skin’s surface. Inert minerals are crystalline substances that lack biological activity and are safe for use on the skin. They serve as abrasive agents that effectively remove dead skin cells, promote cell turnover, and stimulate collagen production.
Commonly used inert minerals in microdermabrasion include:
- Aluminum oxide: Hard and durable, suitable for treating acne, scars, and sun damage.
- Sodium bicarbonate: Gentle and less abrasive, ideal for sensitive skin and superficial exfoliation.
- Calcium carbonate: Soft and fine, suitable for delicate areas like the face and neck.
- Magnesium oxide: Medium hardness, effective for removing blackheads and fine lines.
Design Considerations for Inert Minerals
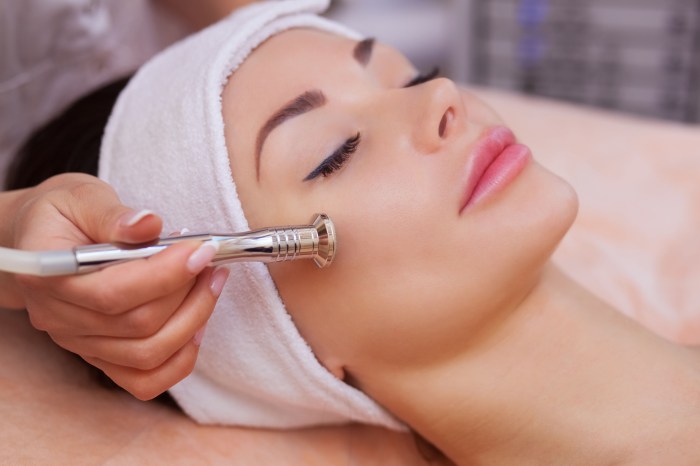

Selecting the appropriate inert minerals for microdermabrasion involves considering several factors:
- Particle size: Smaller particles provide finer exfoliation, while larger particles are more aggressive.
- Shape: Irregular-shaped particles enhance exfoliation, while spherical particles are gentler.
- Hardness: Harder minerals provide deeper exfoliation, while softer minerals are suitable for sensitive skin.
Inert mineral particles for microdermabrasion are typically created through processes such as crushing, grinding, and sieving to achieve the desired size and shape.
Applications of Inert Minerals in Microdermabrasion

Inert minerals are widely used in microdermabrasion for various applications:
- Skin rejuvenation: Removes dead skin cells, revealing brighter and smoother skin.
- Acne treatment: Exfoliates clogged pores, reducing inflammation and preventing breakouts.
- Scar reduction: Stimulates collagen production, helping to improve the appearance of scars.
- Hyperpigmentation treatment: Lightens dark spots and evens out skin tone.
- Wrinkle reduction: Promotes cell turnover and collagen production, minimizing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Case studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of inert minerals in microdermabrasion. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology showed that microdermabrasion using aluminum oxide crystals significantly improved skin texture and reduced acne lesions.
Safety and Precautions: Inert Minerals Designed For Microdermabrasion Use Are Known As

While microdermabrasion using inert minerals is generally safe, there are potential side effects to consider:
- Skin irritation: Mild redness and inflammation may occur, especially with aggressive exfoliation.
- Hyperpigmentation: In rare cases, excessive exfoliation can lead to darkening of the skin.
- Infection: Improper sterilization of equipment can introduce bacteria, leading to infections.
To minimize risks, it is essential to follow proper techniques and precautions:
- Use sterile equipment and avoid over-exfoliation.
- Test the minerals on a small area of skin before applying them to the entire face.
- Apply sunscreen after treatment to protect the skin from sun damage.
- Avoid microdermabrasion if you have active acne, eczema, or other skin conditions.
FAQ Compilation
What are the benefits of using inert minerals in microdermabrasion?
Inert minerals gently remove dead skin cells, promote collagen production, and improve skin texture and tone.
What are the most commonly used inert minerals for microdermabrasion?
Aluminum oxide, sodium bicarbonate, and magnesium oxide are among the most popular inert minerals used in microdermabrasion.
How do I choose the right inert mineral for my microdermabrasion treatment?
Factors to consider include particle size, shape, and hardness. Consult with a qualified skincare professional for guidance.